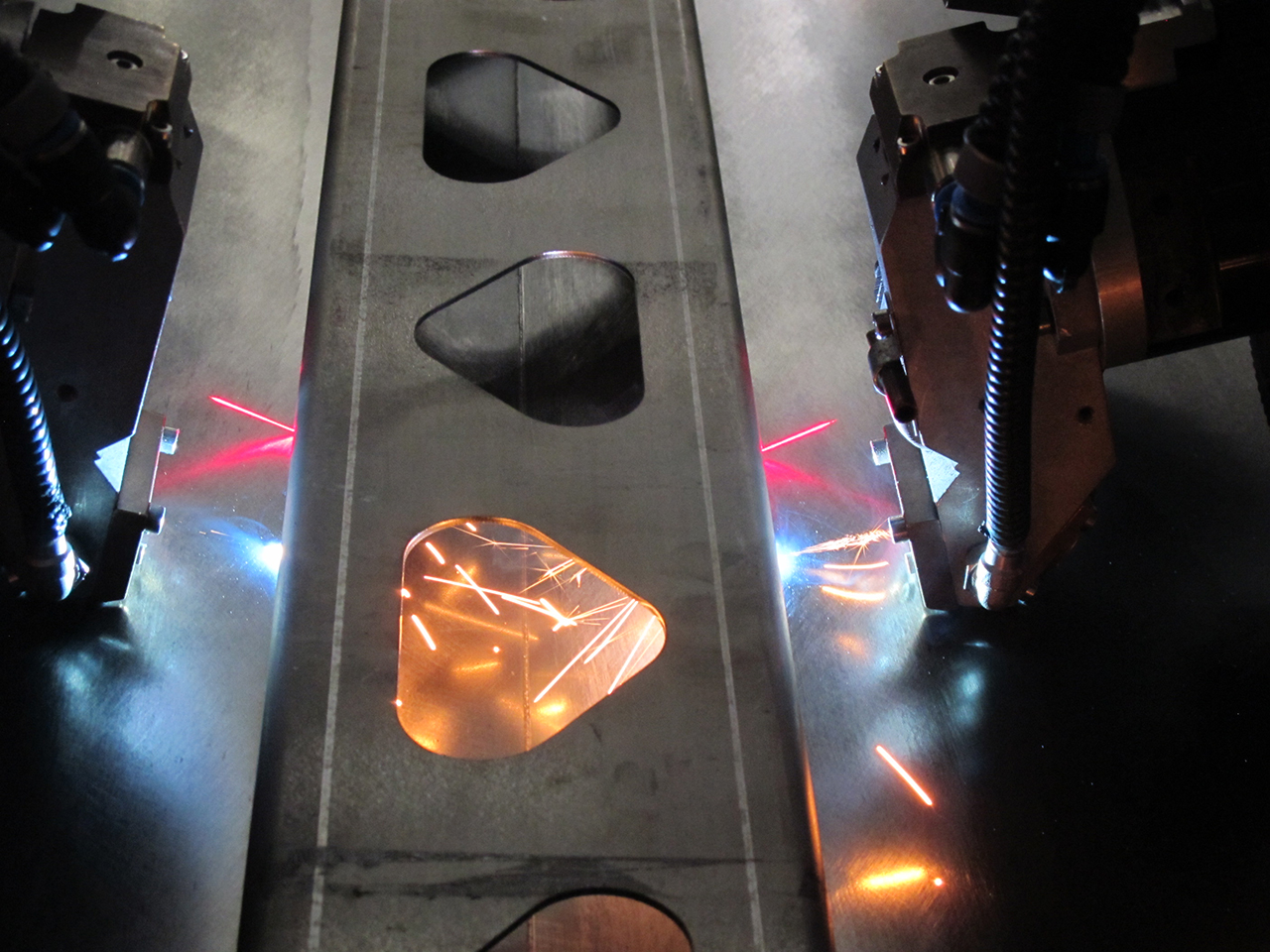
Modern lightweight structure fabricated by simultaneous double-sided, low-distortion laser beam welding; typical applications: Aircraft fuselage, side walls in railcar construction and other large-format structures.
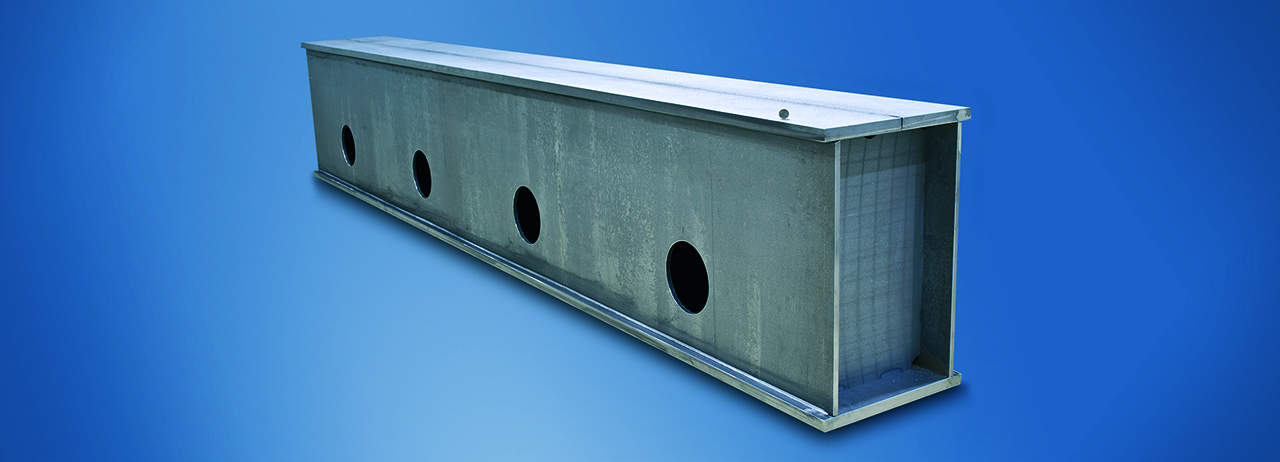

Laser welding of large-format steel structures (4 x 0.75 x 0.5 m³) enables shorter production chains, e.g. by eliminating the need for subsequent straightening work.
The manufacturing processes in steel construction as well as in ship and railway vehicle construction are still characterized by manual and partially automated individual fabrication steps. In order to manufacture large-format and highly stressed steel structures in a high-quality manner, it is not only necessary to have profound technical know-how, but also cost-, energy- and resource-efficient welding processes. Modern joining processes such as laser beam welding will revolutionize steel construction in the coming decades. They contribute to securing the manufactures’ competitiveness by introducing flexible and fully automated processes into production.
Advantages offered by laser beam welding
Material
- Utilization of high-strength steel materials' property potential
- Savings of up to 80 percent on expensive filler materials thanks to very narrow weld seams
Process
- Doubling of welding speed compared to conventional joining processes
- Shortening of the production chain by eliminating preheating and straightening processes
- Use of high-energy and fully automatable welding processes
- Semi-finished metal sheets can still be cut using plasma cutting processes
- High occupational safety due to laser protection directly attached to the welding head - no need for expensive additional equipment (e.g. laser protection walls, enclosures)
- Reduction of a product's CO2 footprint through energy- and resource-efficient processes
Component properties
- Low thermal load on the component during the welding process
- Production of quality-optimized and statically optimized joints
- Sheet thickness-independent, low-distortion welding of corner, T and butt joints
- Reliable gap bridging (two millimeters in the butt joint) at plasma cut edges
Application examples
- High-strength metal structures for ships, rail vehicles and cranes
- Construction machinery: Excavator chassis and gripper arms, agricultural machinery, vehicles for concrete pumping systems
 Fraunhofer Institute for Material and Beam Technology IWS
Fraunhofer Institute for Material and Beam Technology IWS