Development of 30 % Lightweight Electric Vehicle Seat Frame Using HPCi® Connection Technology (JOASIS)
Motivation
The demand for resource-saving production methods and material combinations has increased sharply, especially in recent years. Increased environmental awareness in combination with legal requirements is forcing manufacturers to rethink in the fields of design and production. This is particularly evident in the example of electromobility with its ever-growing sales markets.
In addition to resource-saving production, efficient operation and environmentally compatible recycling at the end of the product life cycle are also in the foreground. The most influential part is operation.
The frequently used integral composite construction and materials such as fiber-reinforced plastic composites are often associated with difficult recyclability and a high overall CO2 footprint. Accordingly, there is a need for lightweight construction and joining concepts that enable the use of sustainable and recycled materials, the manufacture and use of lightweight structures, and complete recyclability at the end of the product life cycle.
Objective and solution approach
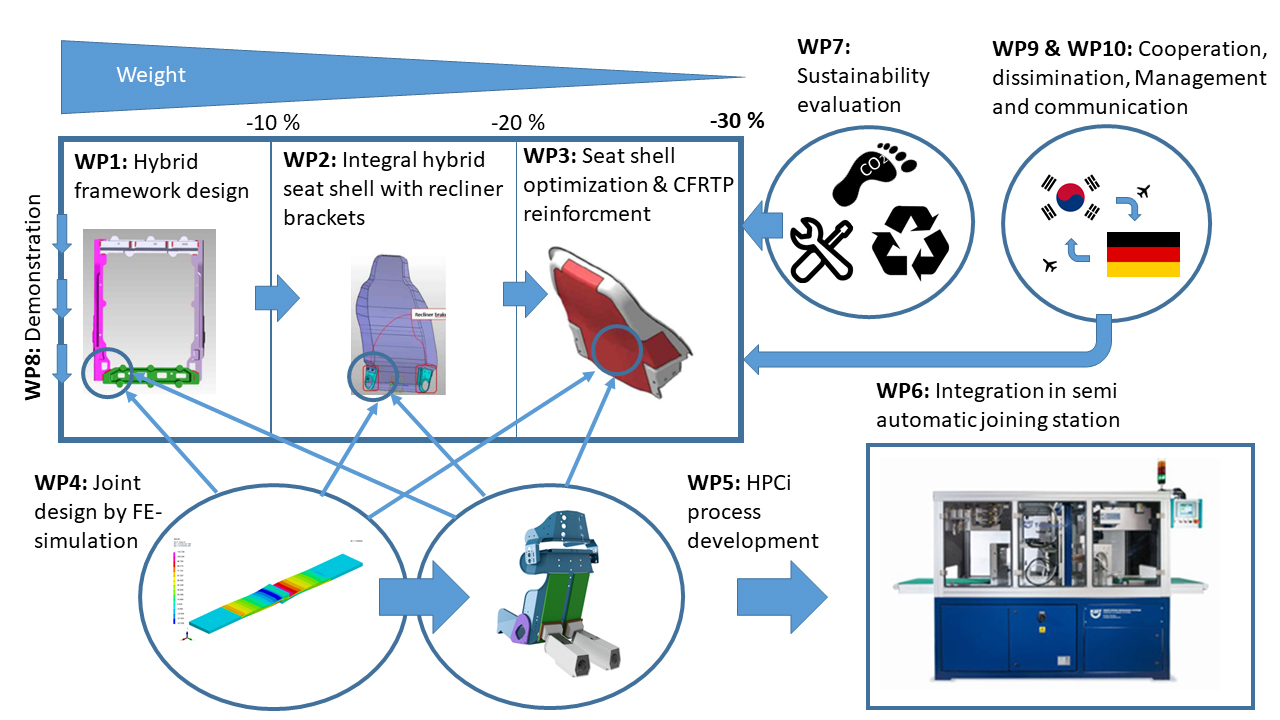
The overall objective of the transnational Korea 2+2 project – JOASIS – is to demonstrate energy and resource efficient production for hybrid lightweight structures while achieving weight savings of up to 30% by using the novel HPCi® joining technology and manufacturing advanced fiber composite components. The project is concerned with the development and manufacture of an automotive lightweight seat structure made of CFRP - recycled material, fiber-reinforced plastic and metal using HeatPressCoolintegrative (HPCi®) joining technology. The overall project focuses on the multi-stage development of a novel disruptive seat design from composite and metal parts, the FE-supported design of the joining interfaces, the development of the joining and disassembly processes, the conception and implementation of a multifunctional joining station and the final production of the prototype seat structures. The project is thus making a significant contribution to strategic cooperation between Germany and Korea with the aim of developing energy- and resource-saving processes and products for greater sustainability and climate protection in the world.
 Fraunhofer Institute for Material and Beam Technology IWS
Fraunhofer Institute for Material and Beam Technology IWS