Hermetic joining of MEMS-based components using reactive multilayer systems (RMS)

Motivation
In microsystems technology, joining processes usually have to cover additional functions, such as hermetic tightness, in addition to a permanent connection between components of an assembly. The joining processes currently in use are sometimes subject to high process temperatures, which lead to thermomechanical stress in the joining zone when different materials with different coefficients of thermal expansion are used. This can be avoided if the temperatures required for the joining process only have a limited effect on the joining point, while the components themselves are spared. This is possible due to the adaptability of reactive multilayer systems.
Aims and procedure
The aim of the research project was to develop joining by means of reactive multilayer systems (RMS) for microsystems technology. The following questions were addressed in particular: Prerequisites for the production of joints with hermetic fine leak tightness as well as basic parameters and conditions for RMS joining.
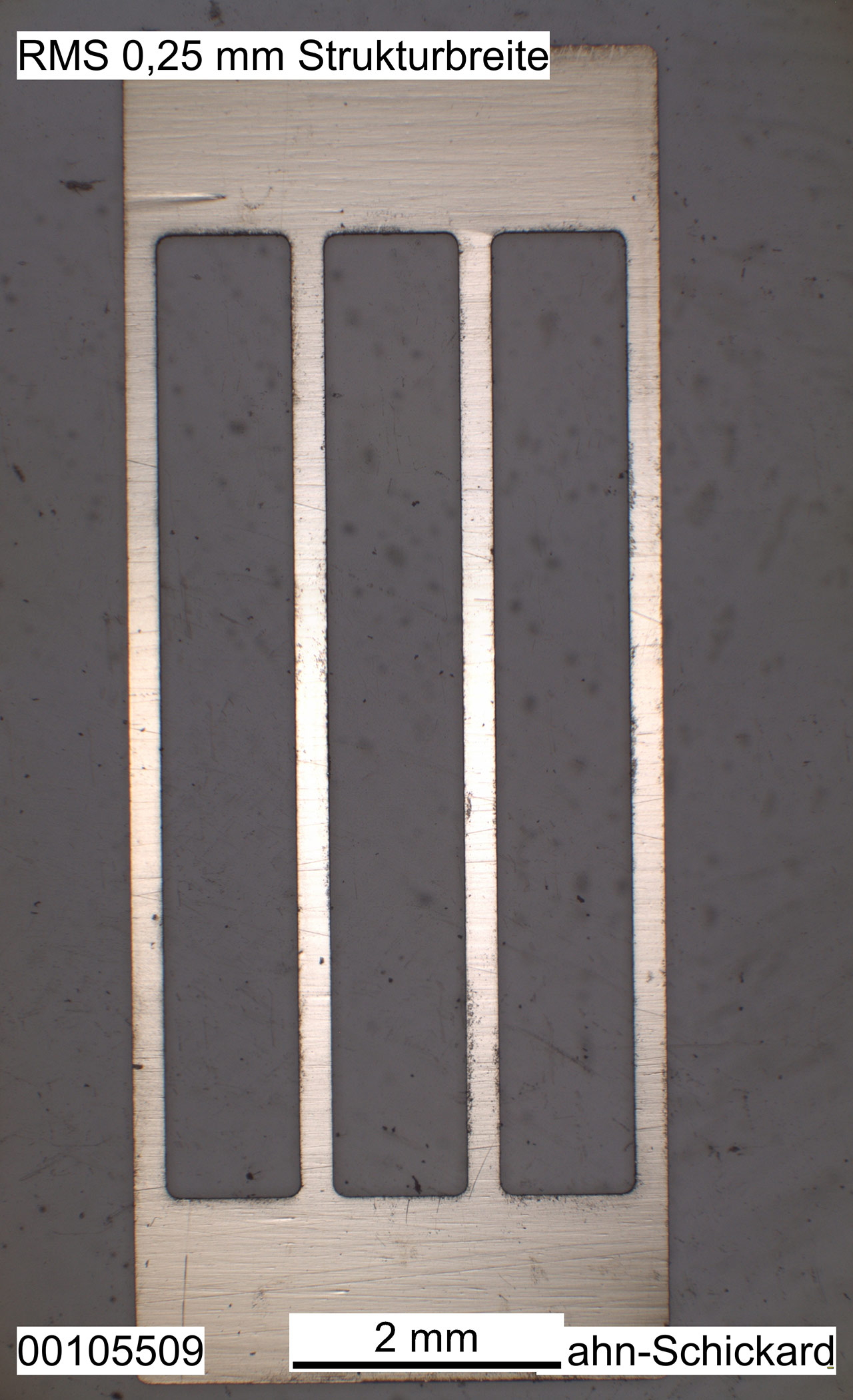
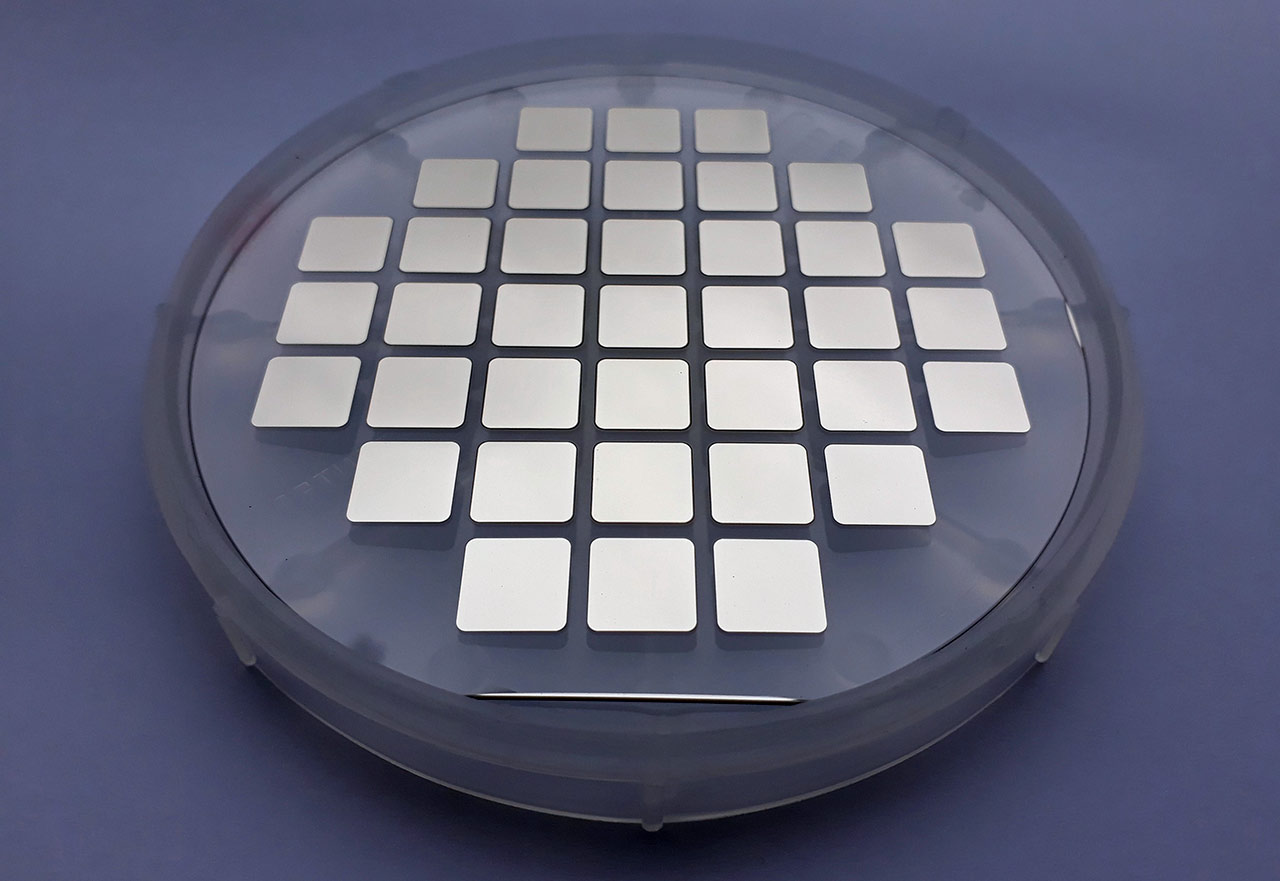
In this research project, both low-crack Ni/Al RMS and high-energy Zr/Si RMS were developed and used to achieve hermetically tight joints. The Zr/Si system offers several advantages in this regard. For example, compared to the Ni/Al system, twice the energy can be released, reducing the layer thicknesses required for joining to a few micrometers. At the same time, this RMS has lower shrinkage, which leads to a minimization of crack formation. For joining tests with test substrates, Zr/Si RMS were produced both as free-standing, optionally pre-soldered films, and in the form of integrated layer systems deposited directly on component and wafer levels [Fig. 1].
Innovation and perspectives
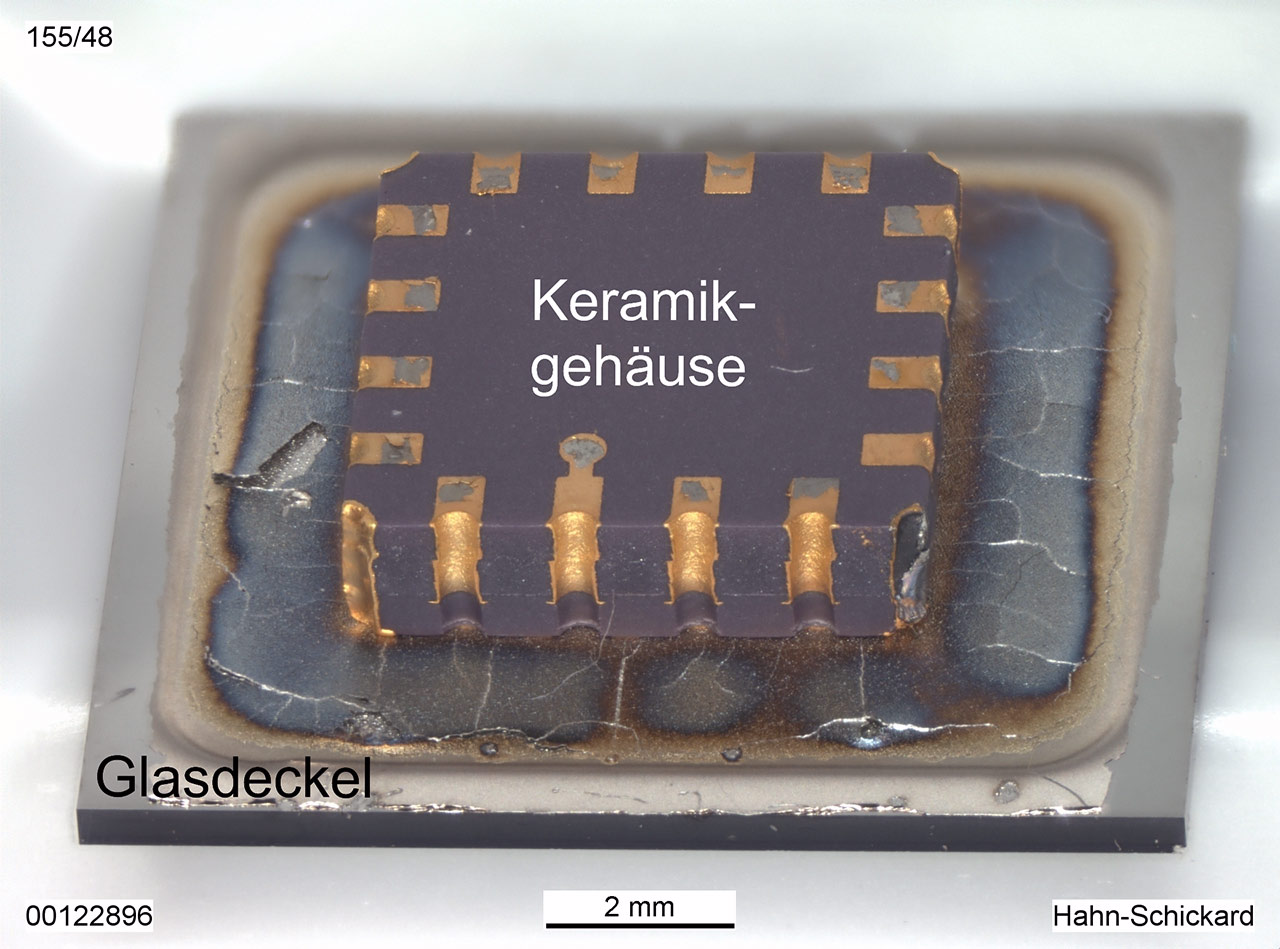
As a result of the research project, it was shown that low-damage and hermetically sealed joints can be created for connections in microsystems technology by adapting the RMS type, their properties with regard to the amount of energy released and reaction temperature, and the joining process technology. The RMS joining technology was implemented on a functional sample from First Sensor Microelectronic Packaging. The factors surface flatness, RMS type, soldering and joining pressure have a decisive influence on the joining properties. No cracks occurred in the glass, and leakage rates of 2•10-8 mbar•l/sec were measured [Fig. 2].
 Fraunhofer Institute for Material and Beam Technology IWS
Fraunhofer Institute for Material and Beam Technology IWS